In the world of mechanical engineering, construction, and product assembly, the choice of Fasteners plays a critical role in performance, durability, and safety. Among the many types of socket cap Screws, two of the most widely used are the Button Head Socket Cap Screws and the Flat Head Socket Cap Screws. At first glance, both may appear similar as precision fasteners, but their design, installation, and applications set them apart.
As industries continue to seek efficiency, strength, and aesthetics in their assembly processes, the question arises: Which one should you choose—Button Head or Flat Head Socket Cap Screws? Let’s dive deeper into their structural differences, advantages, drawbacks, and the decision-making factors for various applications.
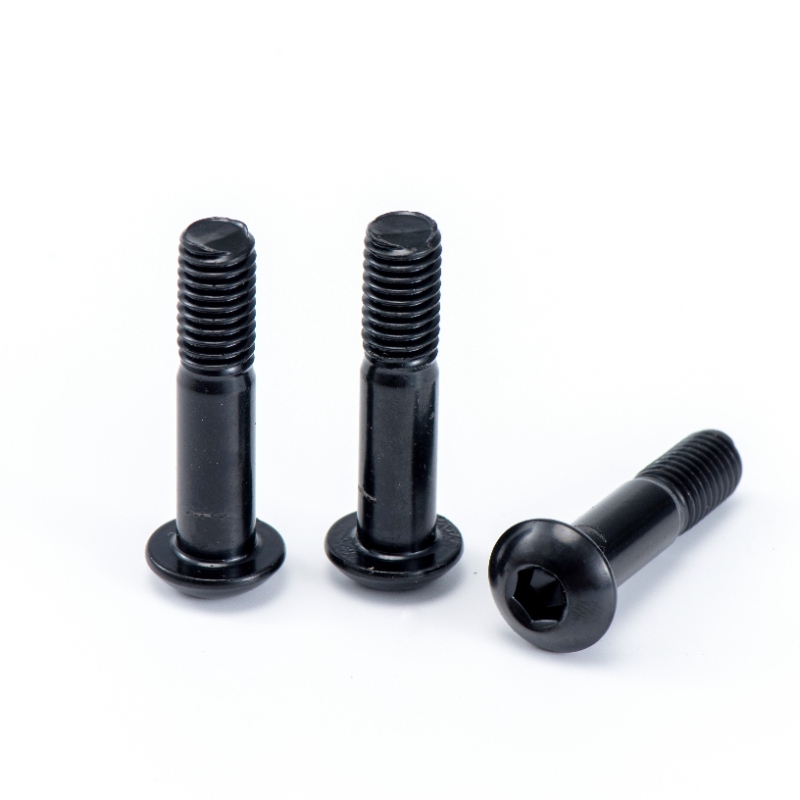

1. Structural Differences
The first and most obvious difference lies in the head design.
Button Head Socket Cap Screws feature a domed, rounded head that sits above the surface when installed. The head is wider in diameter but shallower in height compared to standard socket cap screws, giving it a low-profile yet visible appearance.
Flat Head Socket Cap Screws, on the other hand, are designed with a countersunk head. Once installed into a pre-drilled countersink, the head sits flush with the surface, creating a smooth finish without protrusion.
This structural difference influences not only the appearance but also the performance of each fastener in real-world applications.
2. Installation Considerations
Installation is a critical factor when selecting between button head and flat head screws.
Button Head Screws are easier to install since they do not require countersinking. They can be applied directly into a tapped hole or through-hole with a nut, saving time during assembly. Their larger head provides a broader clamping area, but they will always remain slightly raised above the surface.
Flat Head Screws require a countersink for proper installation. This adds an extra machining step but results in a perfectly flush finish. Flat heads are commonly chosen in applications where clearance is limited, such as in moving machinery parts or aesthetic products where protrusion must be avoided.
From an installation perspective, button heads save labor, while flat heads offer design precision.
3. Strength and Load Distribution
When it comes to performance, load distribution and strength are two critical metrics.
Button Head Socket Cap Screws have a lower head height and reduced depth for the internal hex drive compared to flat heads. While strong, they generally provide lower tensile strength than flat head versions because of the smaller head-to-shank transition area. However, their larger surface contact area helps distribute clamping loads evenly, making them ideal for lighter structural fastening.
Flat Head Socket Cap Screws, with their countersunk design, are engineered for strength. They offer deeper hex drive engagement, enabling higher torque application without stripping. This makes them better suited for high-stress applications requiring superior tensile strength and resistance to shear forces.
In short, button heads excel in moderate-strength applications with aesthetic considerations, while flat heads dominate high-strength, flush-mount applications.
4. Aesthetic and Ergonomic Differences
In industries such as consumer electronics, furniture, and automotive interiors, the look and feel of fasteners matter just as much as their performance.
Button Head Screws are often favored for their rounded, polished look. They provide a sleek finish while still being visible, making them suitable for decorative or visible installations. Their low profile also reduces the chance of snagging compared to standard hex Bolts.
Flat Head Screws disappear into the surface once countersunk, creating a clean, seamless appearance. This is essential in applications like aerospace panels, bicycle components, or electronics enclosures, where both function and aesthetics demand minimal protrusion.
5. Material and Surface Treatment Options
Both button head and flat head socket cap screws are manufactured in various materials, including:
Alloy Steel – offering high tensile strength, often with black oxide finish.
Stainless Steel – corrosion-resistant and ideal for outdoor, marine, or medical applications.
Brass or Titanium – for specialty applications requiring lightweight or non-magnetic properties.
Surface treatments such as zinc plating, black oxide, or nickel plating enhance corrosion resistance. Choosing the right material ensures the screw performs under its intended environmental conditions.
6. Industry Applications
Button Head Socket Cap Screws
Automotive interiors and trim parts
Electronics casings and enclosures
Machinery covers and guards
Furniture assembly
Applications requiring a neat, low-profile but visible fastening solution
Flat Head Socket Cap Screws
Aerospace and defense, where flush installations reduce drag and enhance safety
Machinery with moving parts, where protrusions would interfere with function
Bicycle and motorcycle components requiring strength and streamlined design
Consumer electronics where aesthetics demand smooth surfaces
Industrial equipment requiring high clamping force in limited space
7. Cost and Availability
In terms of cost, button head screws are generally less expensive due to their simpler installation requirements—no countersinking is needed. They are widely available and easy to source in multiple materials and sizes.
Flat head screws, on the other hand, may involve slightly higher costs because of the added countersinking process and the precision required for flush installation. However, in industries such as aerospace or precision engineering, the added expense is justified by the performance benefits.
8. Safety and Performance Standards
Both types of screws are manufactured under international standards such as DIN, ISO, and ANSI. Compliance ensures that the screws meet specific requirements for strength, dimensional accuracy, and performance. For critical applications, especially in aerospace and defense, using certified fasteners is mandatory to guarantee safety and reliability.
9. Decision-Making Guide: Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between button head and flat head socket cap screws ultimately depends on your project’s priorities:
10. Conclusion
In the debate between Button Head Socket Cap Screws and Flat Head Socket Cap Screws, there is no universal winner. Each type has its strengths, weaknesses, and ideal applications. For engineers, designers, and manufacturers, the decision should balance installation efficiency, load requirements, aesthetics, and budget.
As industries evolve toward lightweight, efficient, and visually appealing designs, the demand for both types will continue to grow. By understanding their differences, businesses can make informed choices that improve performance, safety, and overall product quality.
In the end, whether you choose a button head for its sleek appearance and ease of use, or a flat head for its strength and seamless finish, the right fastener will always be the one that aligns best with your application’s needs.