Blind Bolt Rivets: Features, Applications, and Maintenance
Introduction to Blind Bolt Rivets
Blind bolt rivets, also known as Blind Rivets or pop rivets, are specialized mechanical Fasteners designed for applications where access to only one side of the workpiece is available. These fasteners consist of a mandrel and a rivet body, which are installed using a rivet gun that pulls the mandrel to deform the rivet body, creating a secure joint. Blind bolt rivets are widely used in industries ranging from aerospace to construction due to their unique installation capabilities and reliable performance.
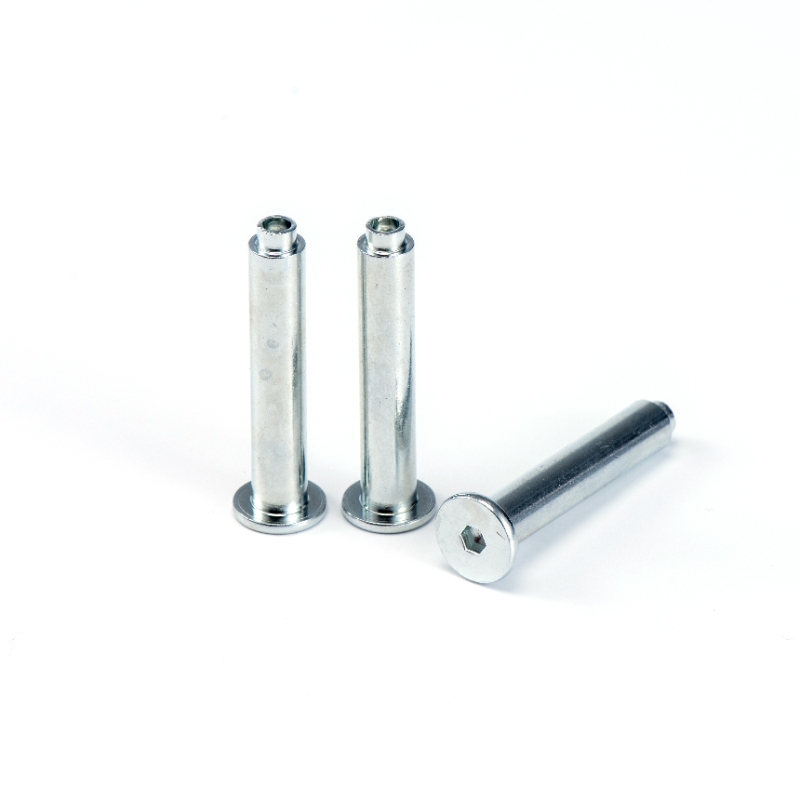

Key Features of Blind Bolt Rivets
1. Single-Side Installation
Blind bolt rivets can be installed from one side of the workpiece, making them ideal for applications where the backside is inaccessible. The installation process requires only 5-15 seconds per rivet depending on size and material.
2. High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Modern Blind Rivets offer impressive strength characteristics. For example, a 1/4-inch diameter aluminum blind rivet can typically withstand 1,200-1,500 lbs of shear load and 600-800 lbs of tensile load.
3. Material Versatility
Available in various materials including:
Aluminum (1100, 5056 grades) with tensile strength of 13,000-45,000 psi
Steel (carbon and stainless) with tensile strength ranging 45,000-125,000 psi
Monel (Nickel-copper alloy) with corrosion resistance and 70,000-80,000 psi tensile strength
Copper with excellent conductivity and 30,000-40,000 psi tensile strength
4. Vibration Resistance
Specialized blind rivets with locking features can withstand vibration frequencies up to 2,000 Hz without loosening, making them suitable for automotive and aerospace applications.
5. Gap Filling Capability
Blind rivets can accommodate varying material thicknesses, typically ranging from 0.020 to 0.375 inches for standard sizes, with some large structural rivets handling up to 1 inch of grip range.
Applications of Blind Bolt Rivets
The unique characteristics of blind bolt rivets make them suitable for numerous industrial applications:
Aerospace Industry
In aircraft manufacturing, specialized aluminum and titanium blind rivets are used for panel assembly with diameters typically between 3/32 to 1/4 inch. These rivets must meet stringent FAA and military specifications (e.g., NASM, MS standards) and often feature flush heads for aerodynamic surfaces.
Automotive Manufacturing
Automakers utilize blind rivets for body panel assembly, interior trim, and chassis components. High-strength steel rivets with M6 to M10 diameters are common for structural applications, while smaller aluminum rivets (3/16 inch) are used for non-structural components.
Construction and Building
In steel frame construction, large diameter (1/2 inch) structural blind rivets provide shear strengths exceeding 10,000 lbs for connecting beams and columns. Aluminum rivets are used for curtain wall systems and roofing applications.
Electronics and Appliances
Small diameter (1/16 to 1/8 inch) blind rivets secure components in electronics enclosures and appliance assemblies where disassembly isn't required. These often use softer materials like aluminum to prevent damage to delicate components.
Marine Applications
Stainless steel and Monel blind rivets with corrosion resistance are used in boat building and offshore structures, typically in 3/16 to 1/4 inch diameters to withstand saltwater exposure.
Maintenance of Blind Bolt Rivets
Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and performance of blind rivet installations:
Inspection Procedures
Visual inspection for corrosion every 6-12 months in normal environments, more frequently in harsh conditions
Check for rivet head deformation indicating loosening (maximum allowable deformation typically 0.002-0.005 inches)
Verify mandrel stem protrusion (should not exceed 1/16 inch beyond rivet head)
Corrosion Prevention
Apply protective coatings (zinc chromate for aluminum, cadmium for steel) when specified
Use compatible materials (e.g., stainless steel rivets with stainless substrates)
In marine environments, consider sacrificial anode protection for critical riveted joints
Replacement Procedures
For damaged rivets:
Drill out the old rivet using a bit 1/64 inch larger than the rivet shank diameter
Remove all debris from the hole
Select a replacement rivet of the same material and 0.002-0.005 inch larger diameter if hole enlargement occurred
Install with proper tooling at recommended pressure (60-100 psi for most pneumatic rivet guns)
Lubrication Requirements
While most blind rivets don't require lubrication after installation, some applications benefit from:
Anti-seize compound on stainless steel rivets (5-10% nickel content compounds recommended)
Dry film lubricants for rivets in high-temperature environments (up to 1,000°F)
Light machine oil (ISO VG 32) on mandrels during installation to reduce tool wear
Storage Recommendations
Proper storage extends shelf life:
Store in original packaging at 40-80°F and 30-50% relative humidity
Separate different materials to prevent galvanic corrosion
Use oldest stock first (typical shelf life 2-5 years depending on material)