Cross Recessed Screws: Technical Specifications and Applications
What Are Cross Recessed Screws?
Cross recessed Screws, commonly known as Phillips Screws, are a type of fastener characterized by a cruciform (cross-shaped) recess in the head. This design was developed by Henry F. Phillips in the 1930s to address the limitations of traditional slotted screws. The cross recess allows for better torque transmission and reduces the likelihood of cam-out (slippage) compared to flathead screws. The most common sizes include #0, #1, #2, #3, and #4, with #2 being the most widely used in general applications.
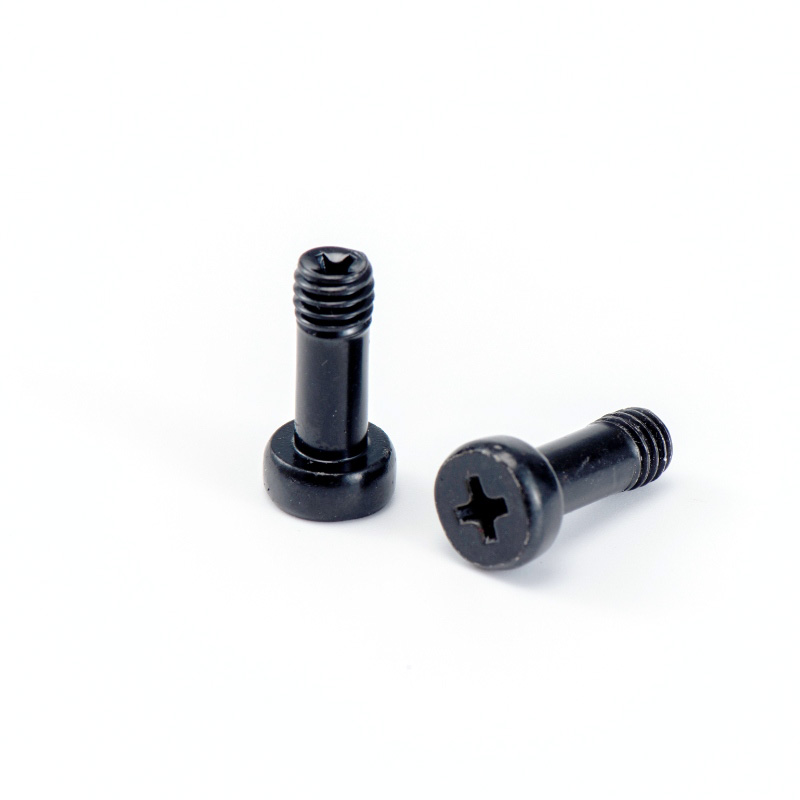

Key technical specifications of cross recessed screws:
Drive Angle: Typically 26° for Phillips heads (compared to 40° for Pozidriv)
Torque Capacity: Ranges from 0.1 Nm (for size #0) to 10 Nm (for size #4) depending on material
Cam-out Prevention: Designed to disengage at approximately 110-130% of recommended torque
Material Strength: Common grades include Grade 2 (tensile strength: 57,000 psi), Grade 5 (120,000 psi), and Grade 8 (150,000 psi)
Head Styles: Pan, flat, oval, and truss heads with diameters ranging from 3mm to 20mm
Key Characteristics and Performance Data
The cross recess design provides several technical advantages. The 26° included angle of the Phillips drive creates a self-centering action, allowing for easier one-handed operation. The flanks of the recess are designed with a radial taper of 6-8°, which helps in distributing stress more evenly during tightening. Modern Phillips screws often feature a JIS (Japanese Industrial Standard) profile with a sharper point angle (90° vs 100° for standard Phillips) for improved engagement.
Performance testing shows that Phillips screws achieve approximately 85-90% drive efficiency when properly matched with the correct driver bit size. The design allows for 20-30% higher torque application compared to slotted screws before cam-out occurs. However, repeated over-torquing can lead to recess deformation, reducing the screw's usable life by up to 40%.
Application Scenarios
Cross recessed screws find applications across numerous industries due to their versatility and ease of use:
Electronics Manufacturing: Size #0 and #1 screws are extensively used in smartphones, laptops, and consumer electronics. The Apple iPhone, for instance, uses Pentalobe and Phillips #000 screws for internal components.
Automotive Assembly: Grade 5 and 8 Phillips screws secure interior trim panels and electrical components. The average modern vehicle contains 150-300 Phillips screws of various sizes.
Aerospace: Special high-strength variants with NASM and MS standards are used in non-critical aircraft components, often made from A-286 stainless steel (tensile strength: 140,000 psi).
Construction: #2 and #3 Phillips screws dominate in drywall installation (with bugle heads) and decking applications. Drywall screws typically have a coarse thread (6-8 TPI) for gypsum board penetration.
Medical Devices: Miniature Phillips screws (size #00 and below) manufactured from 316LVM stainless steel are used in surgical instruments and implantable devices.
Maintenance and Care Procedures
Proper maintenance extends the service life of cross recessed screws and ensures optimal performance:
Driver Bit Selection: Always match the driver bit to the screw size precisely. A #2 Phillips bit should measure approximately 3.3mm across the tips. Worn bits increase cam-out risk by 60% and should be replaced after 5,000-10,000 cycles.
Lubrication: For high-torque applications, apply molybdenum disulfide grease (MoS2) to reduce friction by up to 35%. In marine environments, use lanolin-based coatings to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Cleaning: Remove debris from recesses using a 0.5mm dental pick or compressed air. Ultrasonic cleaning with isopropyl alcohol is effective for precision screws.
Torque Control: Use torque-limiting drivers set to 75-80% of the screw's proof load. For a Grade 2 steel screw, this typically means 2.5-3.5 Nm for a #2 size.
Storage: Store screws in 40-50% RH environments with vapor corrosion inhibitors (VCI). Magnetic organizers can cause residual magnetism in sensitive applications.
Specialized Variants
The Phillips design has evolved to meet specific technical requirements:
Phillips II®: Features ribbed flanks that increase torque capacity by 25% and reduce cam-out incidents
ACR™ (Anti-Camout Recess): Incorporates undercut sidewalls that improve grip by 40% in high-vibration environments
JIS B 1012: Japanese standard with a 90° point angle and deeper recess (0.8mm vs 0.6mm for standard Phillips)
Frearson: British variant with a 45° point angle that doesn't cam out as readily as Phillips