Hexagon Head Screws: Technical Overview and Applications
Hexagon head Screws, commonly referred to as hex Bolts or hex cap screws, are a type of fastener characterized by their six-sided (hexagonal) head. These screws are widely used in industrial, automotive, and construction applications due to their high torque capacity and ease of installation. The hexagon shape provides multiple gripping surfaces, allowing for efficient tightening with wrenches or sockets.
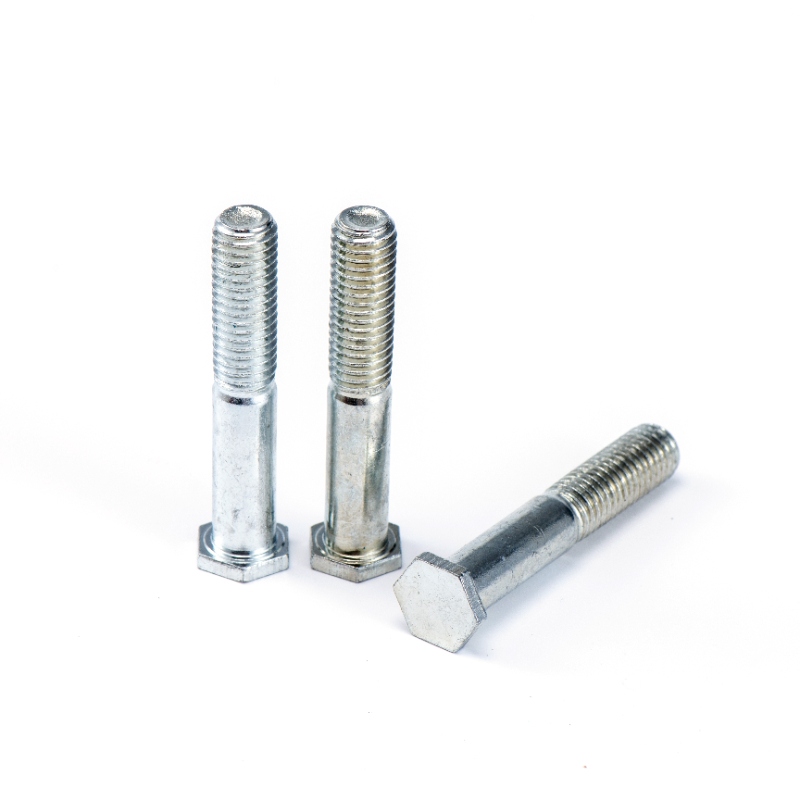

Technical Characteristics
Key Features of Hexagon Head Screws:
Head Dimensions: Standard hex head widths range from 8.1 mm (M5) to 36 mm (M24) across flats, with heights varying from 5.3 mm (M5) to 21.1 mm (M24) according to ISO 4014/4017 standards.
Material Strength: Typically manufactured in strength classes 8.8 (tensile strength: 800 MPa, yield strength: 640 MPa), 10.9 (1000 MPa/900 MPa), and 12.9 (1200 MPa/1080 MPa) for steel variants.
Thread Specifications: Available in metric coarse (standard) and fine thread pitches, with M6 screws having a 1.0 mm pitch (coarse) or 0.75 mm pitch (fine).
Torque Capacity: An M10 grade 8.8 hex bolt can withstand approximately 47 Nm of tightening torque when lubricated, per VDI 2230 guidelines.
Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel variants (A2/A4) offer pitting resistance equivalent (PRE) values of ≥25 for AISI 316 (A4) grade.
Applications
Hexagon head screws find extensive use across multiple industries:
1. Automotive Industry
In vehicle assembly, high-strength hex bolts (10.9 or 12.9 grade) secure critical components like:
Engine blocks (M10-M14 bolts with 100-180 Nm torque specifications)
Suspension components (M12-M16, often with stretch-controlled designs)
Transmission housings (requiring ISO 4762 socket head cap screws for limited clearance)
2. Construction and Structural Engineering
Structural hex bolts comply with ASTM A325 (tensile strength: 120 ksi) or A490 (150 ksi) standards for:
Steel beam connections (typically ¾" to 1½" diameter)
Bridge construction (often with hot-dip galvanized coating ≥85 µm)
Prefabricated concrete elements (using anchor bolts with hex heads)
3. Machinery and Equipment
Industrial machines utilize hex screws for:
CNC machine frames (M8-M20 with DIN 933 full thread specifications)
Pump and compressor assemblies (often with NASM 1312 NAS washers)
Robotic arm joints (frequently employing shoulder screws with hex heads)
4. Aerospace Applications
Specialized hex head Fasteners meet:
NASM 21200 standards for aircraft structural bolts
Material requirements including A286 CRES (140 ksi tensile) or Ti-6Al-4V (130 ksi)
Close-tolerance AN/MS specifications with ±0.0005" diameter control
Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity:
1. Installation Best Practices
Always use calibrated torque wrenches - under/over-torquing by ±15% can reduce joint integrity by 30-40%
Apply appropriate thread lubricants (e.g., molybdenum disulfide paste for high-temp applications)
For critical joints, consider torque-angle method (e.g., 70 Nm + 90° turn)
2. Corrosion Prevention
Marine environments require 316 stainless or Inconel 718 fasteners
Apply zinc flake coatings (5-15 µm) with >1000 hr salt spray resistance
For dissimilar metals, use dielectric grease or Duralac compound
3. Inspection and Replacement
Ultrasonic testing can detect internal cracks in 10.9+ grade bolts
Replace bolts showing >0.2% permanent elongation (measured with micrometers)
In high-vibration environments, consider Nord-Lock washers or Loctite 263 threadlocker
4. Storage Conditions
Maintain <40% relative humidity in storage areas
Organize by ANSI B18.2.1 or DIN 931/933 specifications
For coated fasteners, use VCI paper wrapping for corrosion protection