Countersunk Head Hexagon Socket Screws: A Comprehensive Guide
Countersunk Head Hexagon Socket Screws, also known as flat head socket cap screws or CSK hex socket screws, are precision Fasteners designed for applications requiring a flush surface finish. These screws feature a conical head with a flat top that sits entirely within a countersunk hole, creating a smooth surface when fully installed. The internal hexagon socket (typically sized from 1.5mm to 36mm according to ISO 10664 standards) allows for high torque application using hex keys or Allen wrenches.
Key characteristics include:
Head Angle: Standard 82° (90° for aerospace applications per NASM 21272)
Material Strength: Typically Grade 8.8 (tensile strength of 800 MPa), 10.9 (1000 MPa), or 12.9 (1200 MPa)
Thread Pitch: Available in fine (UNF) and coarse (UNC) threads with pitches ranging from 0.35mm to 4.0mm
Surface Treatment: Common options include black oxide (3-5μm), zinc plating (5-8μm), and Dacromet coating (6-12μm)
Torque Capacity: M6 size (10.9 grade) can withstand approximately 12.5 Nm of tightening torque
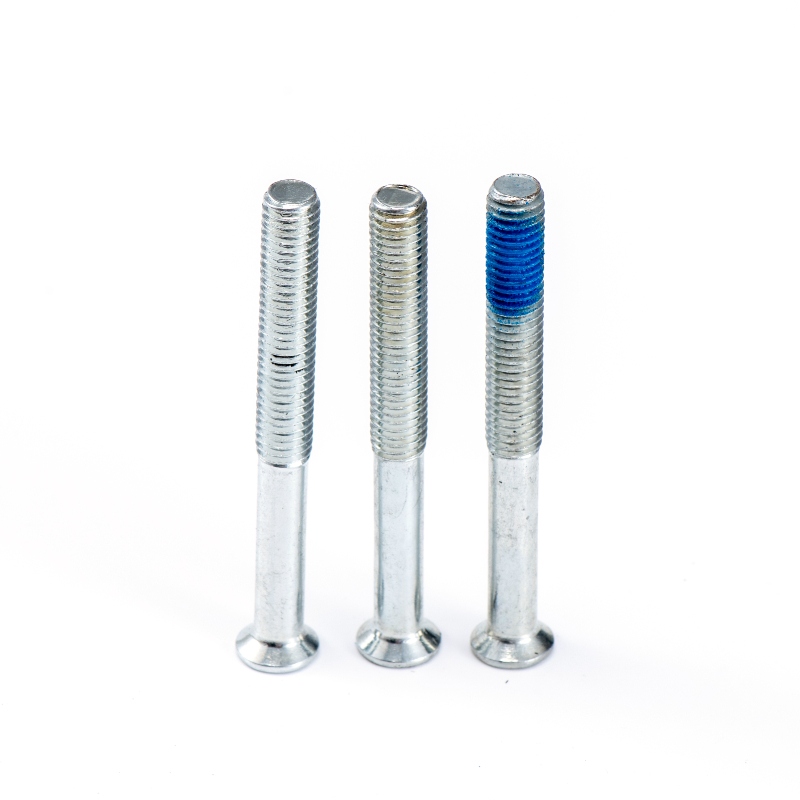

Technical Specifications and Performance Data
The dimensional specifications of these screws follow strict international standards. For metric sizes (DIN 7991), the head diameter (dk) ranges from 3.0mm for M2 screws to 48mm for M24 screws, with a corresponding head height (k) of 1.1mm to 14.4mm. The hex socket depth averages 60-70% of the head height to ensure proper tool engagement.
Mechanical properties are particularly noteworthy. A standard M8x1.25 screw in 12.9 grade alloy steel exhibits:
The countersink angle tolerance is typically held within ±1° for precision applications, while head-to-shank concentricity is maintained at 0.1mm TIR (Total Indicator Reading) or better for high-quality screws.
Primary Application Scenarios
Countersunk Head Hexagon Socket Screws find extensive use across industries where flush mounting and high clamping force are required:
1. Aerospace and Aviation
In aircraft assembly, these screws (often titanium or A286 stainless steel) secure panels and fairings with NASM 21272 specifications. The flush head reduces aerodynamic drag, while the hex socket allows for controlled torque application up to 250 in-lbs in critical joints.
2. Automotive Engineering
Used in engine components, transmission systems, and chassis assemblies. High-performance vehicles employ 12.9 grade screws with lubricated threads (μ≈0.12) to maintain precise preload under vibration.
3. Industrial Machinery
Heavy equipment utilizes large diameter screws (up to M36) with waisted shank designs to improve fatigue resistance in dynamic loading applications.
4. Electronics and Precision Instruments
Miniature versions (M1.6-M3) with non-magnetic properties (A2/A4 stainless) are essential in sensitive electronic enclosures and optical devices.
5. Marine Applications
316 stainless steel variants with 50μm thick Dacromet coating provide corrosion resistance in saltwater environments exceeding 1000 hours in salt spray tests.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper Installation Techniques
Always use undamaged hex keys that fully engage the socket (minimum 90% insertion depth)
For critical applications, apply thread lubricant (e.g., molybdenum disulfide) to achieve consistent preload
Countersink holes should be machined to 82° +0/-1° with surface roughness ≤ Ra 3.2μm
Torque values should follow manufacturer specifications (e.g., M10 10.9 grade: 47 Nm dry, 34 Nm lubricated)
Maintenance Procedures
Regular inspection intervals should include:
Visual checks for corrosion pits >0.1mm deep
Torque verification using calibrated wrench (re-torque after 24-48 hours of initial installation)
Socket condition assessment - replace if hexagon rounding exceeds 5% of nominal size
For long-term storage:
Apply VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper in sealed containers
Maintain relative humidity below 40% at 20°C
Stainless steel screws should be kept separate from carbon steel to prevent galvanic corrosion
Specialized Maintenance for Harsh Environments
In chemical processing plants:
Quarterly inspection for chloride stress corrosion cracking (for 300-series SS)
Apply PTFE-based anti-seize annually on threads
Ultrasonic cleaning every 2 years to remove embedded contaminants